UvA MSc AI students publish paper at ACL
6 July 2023
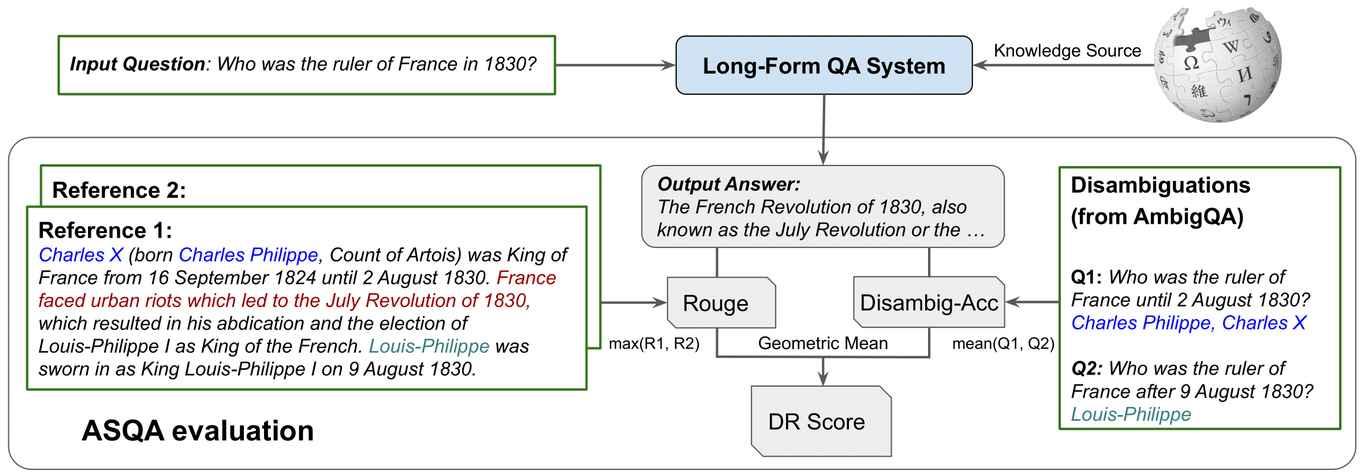
How Do Language Models Handle Ambiguous Question Answering?
Previous research (Krishna et al. 2021) has demonstrated that language models can face difficulties when generating long-form answers that are both coherent and accurate, which indicates the need for further research before they can be reliably deployed in production. To gain insights into the limitations of current approaches, the authors examined how both dataset and model scaling affect the fluency and the comprehensiveness of question-answering (QA) systems. The findings suggest that larger models are more capable of handling complex questions, but due to the limited resources available for ambiguous QA, it remains a challenging domain.
The authors also investigated the alignment of automated metrics with human judgement. While simple string-matching metrics can be easily manipulated, the use of recently proposed metrics (Stelmakh et al. 2022) that rely on neural models to evaluate performance provides a more reliable assessment. Finally, the authors addressed the issue of hallucinations, where models generate responses that is not grounded in facts. They found that this phenomenon is not as prevalent due to the complexity of the task, which makes it difficult for fabricated answers to emerge from a medium-sized model's internal knowledge representation.
Overall, the paper contributes to the ongoing research on the limitations of language modeling and emphasizes the need for further improvements in the performance of these systems.